Latest News
RCIS 2019 Conference Program is available.
RCIS 2019 Accepted papers are available.
RCIS 2019 has received the IEEE Technical Sponsorship.
Registration is open: Register now
Accomodations : Book now
Social Events are updated: Social Events
Important Dates
Conference: May 29th-31st, 2019
Abstract submission deadline:
January 23rd, 2019 February 1st, 2019 Anywhere on Earth”, i.e., UTC-12
January 23rd, 2019 February 1st, 2019 Anywhere on Earth”, i.e., UTC-12
Regular paper submission deadline:
February 1st, 2019 February 10th, 2019 Anywhere on Earth”
February 1st, 2019 February 10th, 2019 Anywhere on Earth”
Notification to authors and registration opening:
March 18th, 2019 April 1st, 2019
March 18th, 2019 April 1st, 2019
Camera-ready copy deadline for all paper types:
April 2nd, 2019 April 12th, 2019
April 2nd, 2019 April 12th, 2019
Author registration deadline:
April 28th, 2019
April 28th, 2019
Twitter
Help us to disseminate #RCIS2019 hashtagRCIS_Conference
Contact
| Organization : Organization committee |
| Webmaster : Samedi Heng |
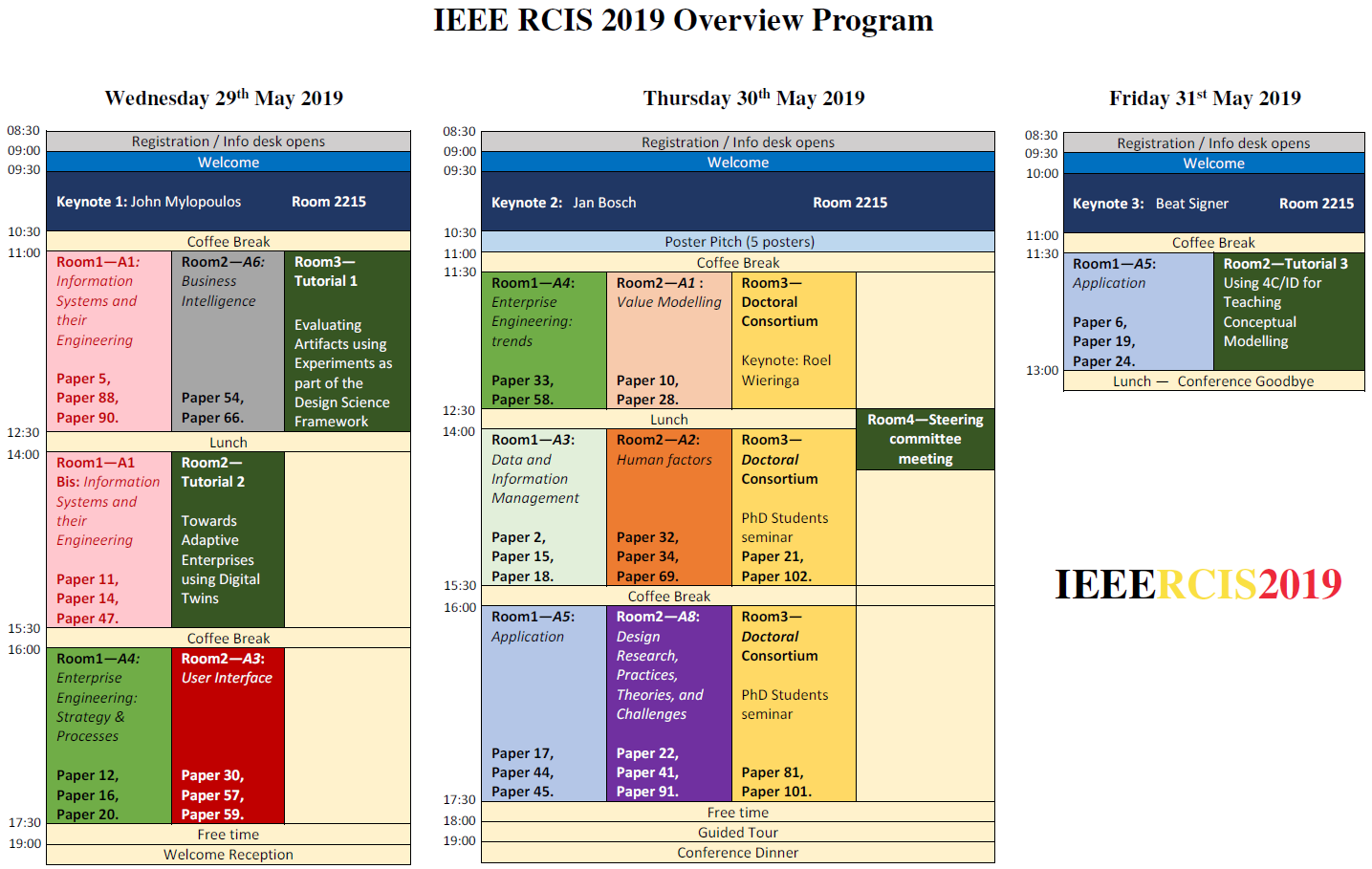
Conference Program
WEDNESDAY MAY 29, 2019
8h30
9h00
9h00
Registration
9h00
9h30
9h30
Welcome
10h30
11h00
11h00
Coffee Break
11h00
12h30
12h30
11h00
11h30
11h30
11h30
12h00
12h00
12h00
12h30
12h30
11h00
12h30
12h30
11h00
11h45
11h45
11h45
12h30
12h30
11h00
12h30
12h30
12h30
14h00
14h00
Lunch break
14h00
15h30
15h30
14h00
14h30
14h30
14h30
15h00
15h00
15h00
15h30
15h30
14h00
15h30
15h30
15h30
16h00
16h00
Coffee break
16h00
17h300
17h300
16h00
16h30
16h30
16h30
17h00
17h00
17h00
17h30
17h30
16h00
17h30
17h30
16h00
16h30
16h30
16h30
17h00
17h00
17h00
17h30
17h30
17h30
19h00
19h00
Free time
19h00
--
--
Welcome ReceptionPlace : Comics Art Museum Brussels
THURSDAY MAY 30, 2019
8h30
9h00
9h00
Registration
9h00
9h30
9h30
Welcome
9h30
10h30
10h30
10h30
11h00
11h00
11h00
11h30
11h30
Coffee Break
11h30
12h30
12h30
11h30
12h00
12h00
12h00
12h30
12h30
11h30
12h30
12h30
11h30
12h00
12h00
12h00
12h30
12h30
12h30
14h00
14h00
Lunch break
12h30
15h00
15h00
14h00
15h30
15h30
14h00
14h30
14h30
14h30
15h00
15h00
15h00
15h30
15h30
14h00
15h30
15h30
14h00
14h30
14h30
14h30
15h00
15h00
15h00
15h30
15h30
14h00
15h30
15h30
14h00
14h10
14h10
14h10
14h30
14h30
14h30
15h00
15h00
15h00
15h30
15h30
15h30
16h00
16h00
Coffee Break
16h00
17h30
17h30
16h00
16h30
16h30
16h30
17h00
17h00
17h00
17h30
17h30
16h00
17h30
17h30
16h00
16h30
16h30
16h30
17h00
17h00
17h00
17h30
17h30
16h00
17h30
17h30
16h00
16h30
16h30
16h30
17h00
17h00
17h00
17h20
17h20
17h20
17h30
17h30
17h30
18h00
18h00
Free time
18h00
19h00
19h00
Guided Tour
19h00
--
--
Conference DinnerPlace : La Manufacture
FRIDAY MAY 31, 2019
8h30
9h30
9h30
Registration
9h30
10h00
10h00
Welcome
10h00
11h00
11h00
11h00
11h30
11h30
Coffee Break
11h30
13h00
13h00
11h30
12h00
12h00
12h00
12h30
12h30
12h30
13h00
13h00
11h30
13h00
13h00
13h00
--
--
Lunch and Conference Goodbye